For my first official post (The intro post doesn’t count) I decided to dive into data structures! Yay!
It took me some time to fully grasp the importance of mastering the fundamentals of data structures. The further I get in my studies, the more I realize how important it is to get very comfortable with data structures. Dedicating time to learning all of the inner workings has helped me see the “big picture” of computer science. Without the big picture, many things can seem pointless and it’s difficult to tie everything together so let’s dive right in.
What in the world is a Data Structure?
A data structure is essentially a method in which data is stored and organized within a computer. Computers have to continuously access, manipulate, save, and delete data. So, data structures were created for computers to perform these tasks quickly and efficiently. There are many different kinds of data structures, each with its own set of features, applications, pros, and cons.
This is why learning data structures is very important. You have to understand them so when you program, you’re able to make the best and most educated decision on how you are handling your data. As we know, nowadays there is SO much data out there, much of it is sensitive. Being educated in this subject as a computer scientist is extremely important so you can handle data effectively and securely.
Linear vs Non-Linear Data Structure
Data Structures can be divided up into many different subcategories but for now we’ll divide them into two, Linear and Non-Linear.
Linear Data Structure
- A linear data structure will store your data in a sequence (linearly :)). In this type of DS, elements have a set order to them. This can be an advantage because all elements could be traversed in a single run. But once the data structure reaches a certain size, it can become inefficient.
- Static: A static data structure has a specified size that cannot be changed. This helps find elements a lot faster but you have to worry about not having enough space.
- Dynamic: A dynamic data structure does not have a specific size and the size can be changed even during runtime. This is helpful when you don’t know the total size of the data beforehand.
Non-Linear Data Structure
- A non-linear data structure does not follow a sequence, instead these data structures have their own hierarchy that they follow. Each with its own advantages and disadvantages depending on your data and what you want to do with it.
Data Structure examples
Here are a few examples of common data structures. This is a very brief description and I’ll talk more in depth on these data structures and others in future posts.
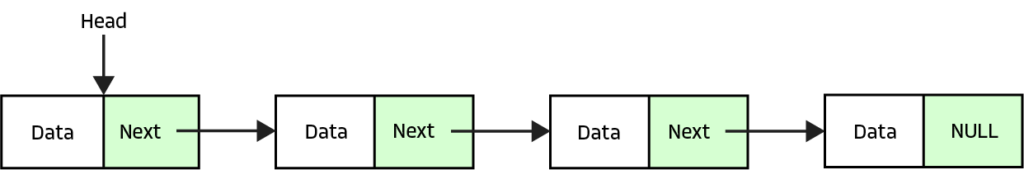
Linked List
This is a linear data structure so all elements have a sequential order. An element, or node, within a linked list holds the data and additionally the address to the next node in the sequence. A pointer is used to hold the address to the next node on the list.
There are many different types of linked lists each with its own pros and cons. Linked lists can be used to build other kinds of data structures like a stack or a queue.
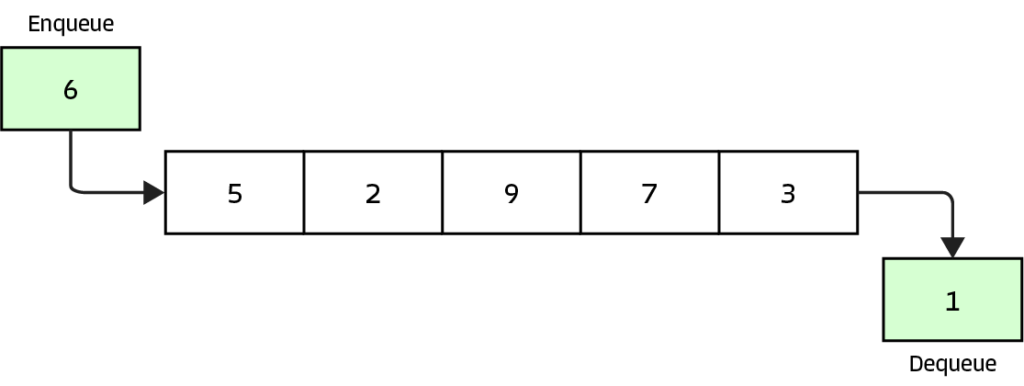
Queue
This is a linear data structure so of course, it follows a specific sequence. When data is inserted into a queue it is done on one side. The deletion of an element is done on the opposite side. This is called the First In First Out (FIFO) order. It pretty much works exactly how a waiting line at the grocery store works. First person that lines up is the first person to get out.
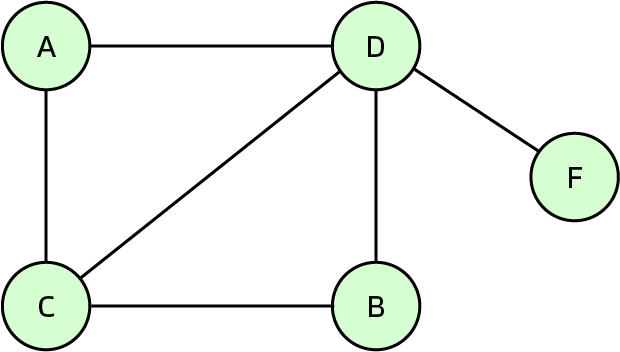
Graph
A graph is a non-linear data structure so it follows its own hierarchy. A graph is made up of nodes, or vertices, and they are linked together with edges. These vertices can be connected to none or many other vertices using these edges. There are many ways these graphs can be arranged.
Why?
While I was learning this I had no clue what the point of any of this was. This seemed so abstract to me that I couldn’t even imagine what data structures would be used for. Learning about data structures and understanding how they work will help you choose the best one for your project.
We use data structures all the time. For example, many social media sites use linked lists for your content feed. Your favorite music player (Spotify, Apple music, Pandora) all use a linked list for when you want to skip to the next song or go back to the previous one. A graph is used in your maps application when you’re trying to find the fastest route to your destination. There is just so much abstraction that it seems like magic. Here are a few more real world examples:
- Graphs are used for phone networks, internet networks, and social media applications.
- Queues are used when sending emails, uploading photos, and handling traffic on a website.
- Hash Tables are used to encrypt passwords and finish your search when typing on google chrome.
Resources
Below are some resources that I used when I was first learning about data structures and helped me write this.
- Data structures – geeksforgeeks
- Intro to Data Structures – geeksforgeeks
- What are Data Structures – Programiz
- Data Structures Tutorial – tutorialspoint
- DSA Intro – freecodecamp
And there we have it—a peek into the extensive world of data structures. Hopefully this post has shed light on some of the most foundational concepts of computer science. But this is only the beginning. Stay tuned for upcoming deep dives into coding, algorithms, and more data structures. Comment any thoughts, questions, or specific topics you’d like me to cover below! Thank you for reading and being a part of this journey!
For more updates, tech insights, and behind-the-scenes content, follow our Instagram account @elcyber.cpp. Click the Instagram icon on the top right to visit our page.